As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, solar panels have become a popular choice for homeowners and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy costs. However, it’s important to understand that solar panels are just one component of a complete solar power system, also known as a solar plant. A solar plant includes other essential elements such as inverters, mounting systems, batteries (for storage), and wiring, all of which work together to generate and deliver clean energy.
Additionally, solar panels are not limited to rooftop installations. They can be installed in a variety of locations depending on your needs, available space, and energy goals. From ground-mounted systems to solar carports and even building facades, the versatility of solar panels makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
In this guide, we’ll break down the different types of solar panels, their pros and cons, applications, and help you make an informed decision for your home or business.
Where Can Solar Panels Be Installed?
Solar panels can be installed in various locations, depending on your property, energy needs, and preferences. Here are some common installation options:
- Rooftops: The most common location for residential and commercial solar installations. Rooftops provide ample space and are often unobstructed by shade.
- Ground-Mounted Systems: Ideal for properties with large open spaces, such as farms or rural areas. Ground-mounted systems can be adjusted for optimal sun exposure.
- Solar Carports: These are elevated structures that provide shade for vehicles while generating solar energy. Perfect for parking lots or driveways.
- Building Facades: Solar panels can be integrated into the exterior walls of buildings, especially with colored or thin-film panels, to maintain aesthetics while generating energy.
- Agricultural Fields: Solar panels can be installed above crops in a practice known as agrivoltaics, which allows for dual land use.
- Floating Solar Farms: Solar panels can be installed on bodies of water, such as lakes or reservoirs, to save land space and reduce water evaporation.
- Portable Solar Systems: Lightweight and flexible panels can be used for camping, RVs, or emergency power needs.
- Half-Cut Solar Panels: A newer technology where solar cells are cut in half, improving efficiency and durability. These panels are suitable for rooftops, ground-mounted systems, and commercial installations.
Now that you know the versatility of solar panel installations, let’s dive into the different types of solar panels available.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels

Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single, pure silicon crystal, which gives them a distinctive black appearance. They are known for their high efficiency and sleek design.
Pros:
- High Efficiency: Monocrystalline panels have the highest efficiency rates (typically 15-22%), making them ideal for homes or businesses with limited roof space.
- Long Lifespan: These panels often come with warranties of 25 years or more.
- Space-Efficient: They require less space compared to other types of panels due to their high efficiency.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Monocrystalline panels are more expensive than other types.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Their performance can decrease slightly in extremely high temperatures.
Applications:
- Residential Rooftops: Ideal for homes with limited roof space due to their high efficiency.
- Commercial Buildings: Suitable for businesses looking to maximize energy output in constrained areas.
- Off-Grid Systems: Perfect for remote locations where space and efficiency are critical.
Best For: Homeowners and businesses with limited space who want maximum efficiency and are willing to invest in a premium product.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
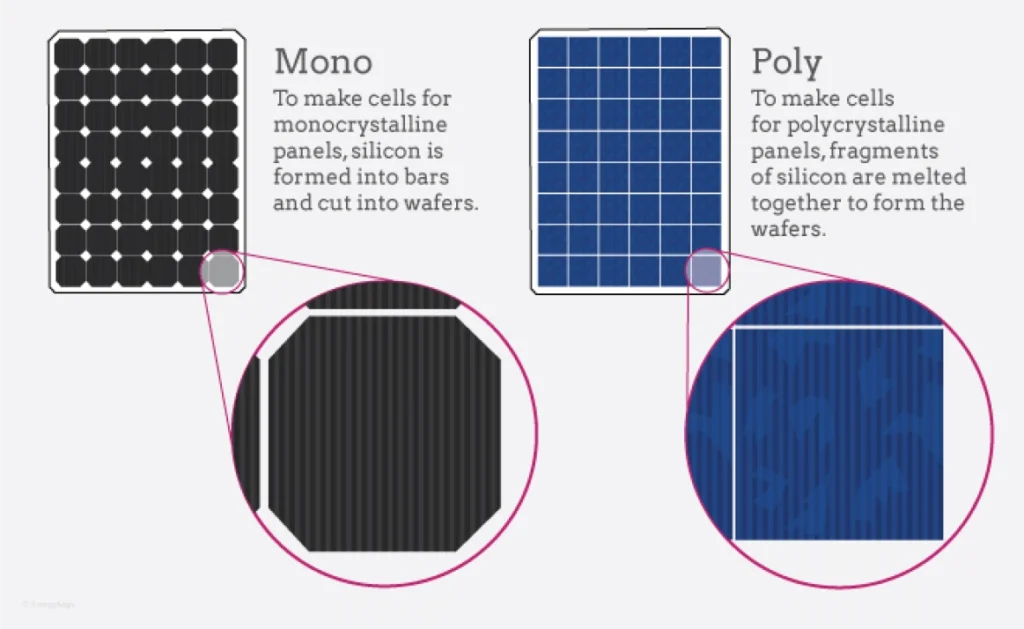
Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple silicon crystals melted together. They have a blue hue and are less efficient than monocrystalline panels but are more affordable.
Pros:
- Lower Cost: Polycrystalline panels are more budget-friendly than monocrystalline panels.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: The production process generates less waste compared to monocrystalline panels.
Cons:
- Lower Efficiency: Efficiency rates typically range from 13-16%, requiring more space to generate the same amount of power.
- Shorter Lifespan: They may have a slightly shorter lifespan compared to monocrystalline panels.
Applications:
- Large-Scale Residential Installations: Suitable for homes with ample roof space.
- Agricultural Facilities: Used in farms and greenhouses where space is not a constraint.
- Community Solar Projects: Cost-effective for large-scale solar farms.
Best For: Budget-conscious homeowners or businesses with ample roof space.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made by layering photovoltaic material (such as amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, or copper indium gallium selenide) onto a surface like glass, metal, or plastic. They are lightweight and flexible.
Pros:
- Lightweight and Flexible: Thin-film panels are easy to install on curved or irregular surfaces.
- Cost-Effective: They are generally cheaper to produce than crystalline panels.
- Performs Well in Low Light: Thin-film panels perform better in low-light conditions compared to crystalline panels.
Cons:
- Lower Efficiency: Efficiency rates are typically between 10-13%, requiring more space.
- Shorter Lifespan: They degrade faster than crystalline panels and often come with shorter warranties.
Applications:
- Commercial Rooftops: Ideal for large, flat commercial roofs.
- Portable Solar Devices: Used in portable solar chargers and small-scale applications.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Integrated into building materials like windows or facades.
Best For: Large commercial projects or installations where weight and flexibility are important factors.
4. Bifacial Solar Panels

Bifacial solar panels can capture sunlight on both sides of the panel, increasing their energy output. They are often used in ground-mounted systems or commercial installations.
Pros:
- Higher Energy Output: Bifacial panels can generate up to 30% more energy than traditional panels.
- Durable: They are often made with tempered glass, making them more resistant to damage.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Bifacial panels are more expensive than traditional panels.
- Installation Complexity: They require specific mounting systems to maximize their dual-sided energy capture.
Applications:
- Solar Farms: Ideal for ground-mounted systems in large open areas.
- Carports and Canopies: Used in structures where sunlight can be captured from both sides.
- Industrial Facilities: Suitable for businesses with large open spaces.
Best For: Large-scale commercial or industrial projects with ample ground space.
5. PERC Solar Panels
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) solar panels are an advanced version of monocrystalline panels. They feature an additional layer on the back of the cell that reflects light back into the cell, increasing efficiency.
Pros:
- Higher Efficiency: PERC panels can achieve efficiency rates of up to 23%.
- Better Performance in Low Light: They perform well in low-light conditions and high temperatures.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: PERC panels are more expensive than standard monocrystalline panels.
- Potential Degradation: The additional layer can sometimes lead to faster degradation over time.
Applications:
- High-Efficiency Residential Systems: Perfect for homeowners looking to maximize energy production.
- Commercial Rooftops: Suitable for businesses with limited space but high energy needs.
- Off-Grid Applications: Ideal for remote locations requiring high efficiency.
Best For: Homeowners and businesses looking for high-efficiency panels with advanced technology.
6. Solar Shingles
Solar shingles are a newer technology that integrates solar cells into roofing materials. They are designed to look like traditional roof shingles while generating electricity.
Pros:
- Aesthetic Appeal: Solar shingles blend seamlessly with the roof, making them ideal for homeowners concerned about aesthetics.
- Dual Functionality: They serve as both a roofing material and a solar panel.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Solar shingles are significantly more expensive than traditional solar panels.
- Lower Efficiency: They are less efficient than traditional panels, typically around 14-18%.
Applications:
- Residential Roofing: Ideal for new home constructions or roof replacements.
- Historic Homes: Suitable for properties where traditional panels may not be aesthetically pleasing.
- Urban Areas: Perfect for homes in densely populated areas with strict aesthetic guidelines.
Best For: Homeowners who prioritize aesthetics and are willing to pay a premium for a sleek, integrated look.
7. Perovskite Solar Panels
Perovskite solar panels are a cutting-edge technology that uses perovskite-structured materials as the light-absorbing layer. They are still in the research and development phase but show great promise for the future.
Pros:
- High Efficiency Potential: Lab tests have shown efficiency rates exceeding 25%.
- Low-Cost Production: Perovskite materials are cheaper to produce than silicon.
- Flexibility: Can be manufactured as thin, lightweight, and flexible panels.
Cons:
- Durability Issues: Perovskite panels degrade faster than traditional panels.
- Commercial Availability: Not yet widely available for residential or commercial use.
Applications:
- Emerging Technologies: Potential use in portable solar devices and wearable technology.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Could be integrated into windows or facades in the future.
- Large-Scale Solar Farms: May become a cost-effective option for utility-scale projects.
Best For: Early adopters and tech enthusiasts keeping an eye on future solar innovations.
8. Colored Facade Panels

Colored facade panels are a type of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) designed to blend seamlessly with the architectural design of a building. They can be customized in various colors and patterns to match the building’s aesthetics while generating electricity.
Pros:
- Aesthetic Integration: Can be customized to match the building’s design, making them ideal for modern architecture.
- Dual Functionality: Serve as both a building facade and a solar energy generator.
- Energy Efficiency: Generate clean energy while reducing the building’s overall energy consumption.
Cons:
- Lower Efficiency: Colored panels typically have lower efficiency compared to traditional solar panels due to the use of filters or coatings.
- Higher Cost: Customization and integration into building designs can increase costs.
Applications:
- Commercial Buildings: Ideal for office buildings, hotels, and retail spaces where aesthetics are important.
- Residential Homes: Suitable for modern homes with a focus on design and sustainability.
- Public Buildings: Perfect for museums, schools, and government buildings looking to showcase green technology.
Best For: Architects, designers, and property owners who prioritize aesthetics and want to integrate solar energy into their building’s design.
9. Half-Cut Solar Panels
Half-cut solar panels are a newer technology where traditional solar cells are cut in half using a laser. This design reduces energy losses and improves efficiency, especially in partially shaded conditions.
Pros:
- Higher Efficiency: Half-cut panels can achieve higher efficiency rates compared to traditional panels.
- Better Performance in Shade: They perform better in partially shaded conditions, making them ideal for areas with intermittent shading.
- Durability: The design reduces stress on the cells, leading to a longer lifespan.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Half-cut panels are generally more expensive than traditional panels.
- Installation Complexity: They may require specialized mounting systems.
Applications:
- Residential Rooftops: Ideal for homes with partial shading or limited roof space.
- Commercial Installations: Suitable for businesses looking to maximize energy output in constrained areas.
- Ground-Mounted Systems: Perfect for large open areas where shading is a concern.
Best For: Homeowners and businesses looking for high-efficiency panels that perform well in partially shaded conditions.
How to Choose the Right Solar Panel for Your Needs
When selecting solar panels, consider the following factors:
- Budget: Determine how much you’re willing to invest upfront and long-term.
- Space: Assess the available space for installation.
- Energy Needs: Calculate your energy consumption to determine the size of the system you need.
- Aesthetics: Consider the appearance of the panels, especially if they will be visible.
- Local Climate: Some panels perform better in specific weather conditions.
Why Choose Solaron.am?
At Solaron.am, we specialize in providing high-quality solar solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce your energy bills or a business aiming to go green, our team of experts will guide you through the process—from selecting the right panels to installation and maintenance.
Conclusion
Investing in solar panels is a smart decision for both homeowners and businesses. By understanding the different types of solar panels and their unique advantages, you can choose the best option for your energy needs and budget. Ready to make the switch to solar? Contact Solaron.am today for a free consultation and take the first step toward a sustainable future!